Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) Fuel Cell
Polymer Electrolyte Membrane (PEM) fuel cell directly converts chemical energy of a fuel into electricity by the reaction of hydrogen with oxygen over a proper catalyst with water as by product. The heart of a PEM fuel cell is the membrane electrode assembly (MEA), which includes the membrane, the catalyst layers, and gas diffusion layers (GDLs). Each GDL is typically composed of a sheet of porous carbon paper in which the carbon fibers are partially coated hydrophobic PTFE, which prevents “flooding” due to excessive water buildup.
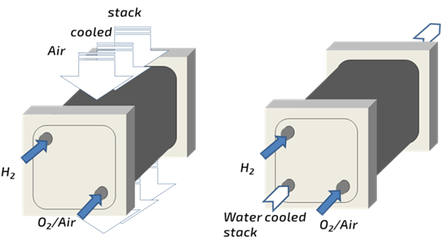
Hardware components include gaskets, which provide a seal around the MEA to prevent leakage of gases, and bipolar plates, which contain flow field channels to allow gases to flow over the MEA.
A single cell produces 0.6–0.8 V under typical operating conditions. To obtain higher voltages, multiple MEAs are usually connected into a fuel cell stack to provide a usable output voltage. Additional cooling channels inside each plate may be used to support air or liquid coolant.
PEM fuel cells need sufficient moisture content for effective proton transfer from anode to the cathode. Thus, it is required that the gases supplied to the PEM fuel cell are humidified either externally or internally to maintain the required moisture content in the membrane and to get stable power output.
For water management, the GDL is coated with a thin layer of high-surface-area carbon mixed with PTFE, called the microporous layer. The microporous layer can help adjust the balance between water retention and water removal.
Hardware components include gaskets, which provide a seal around the MEA to prevent leakage of gases, and bipolar plates, which contain flow field channels to allow gases to flow over the MEA.
A single cell produces 0.6–0.8 V under typical operating conditions. To obtain higher voltages, multiple MEAs are usually connected into a fuel cell stack to provide a usable output voltage. Additional cooling channels inside each plate may be used to support air or liquid coolant.
PEM fuel cells need sufficient moisture content for effective proton transfer from anode to the cathode. Thus, it is required that the gases supplied to the PEM fuel cell are humidified either externally or internally to maintain the required moisture content in the membrane and to get stable power output.
For water management, the GDL is coated with a thin layer of high-surface-area carbon mixed with PTFE, called the microporous layer. The microporous layer can help adjust the balance between water retention and water removal.